November 14, 2014
Elemental Technology for High-energy-density Lithium Ion Batteries that Doubles Electric Vehicle Driving Range
Hitachi, Ltd. announced the development of a battery technology that doubles the driving distance of electric vehicles.
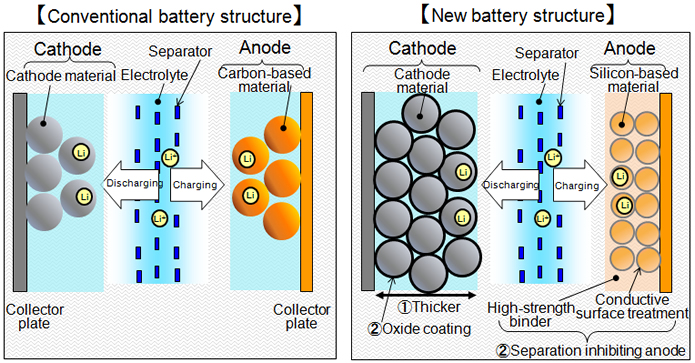
Specifically, the electrode is twice the thickness of conventional batteries, thus increasing the amount of lithium-ion's available for charging and discharging and increasing the energy density. Another feature is optimization of the distribution of the active material within the electrodes to promote lithium-ion mobility and increase battery power density. That was achieved by using a newly developed technique for three-dimensional visualization of electrode structure to clarify lithium-ion movement.
Silicon-based anode materials are capable of charging and discharging more lithium ions than conventional carbon-based materials, but they have a short service life because they are easily separated from the electrode. We have developed a technique for strongly binding silicon materials to the electrode to suppress that separation, thus achieving the service life that is about the same as carbon-based materials. Another problem with conventional anode materials is that application of a high voltage causes decomposition of the electrolyte, shortening the service life. We were able to overcome that problem and extend lifetime by coating the cathode surface with oxide. By applying these solutions, we were able to achieve high energy density and power density together with a long service lifetime, resulting in batteries that can double the driving range of electric vehicles.