The pharmaceutical industry value chain is ushering in a period of major change in the lead up to the full commercialization of regenerative medicine and related products. Hitachi has been participating in collaborative creation with pharmaceutical manufacturers and wholesalers, working to facilitate DX in customer operations along the value chain for these products and developing DX solutions that are based around its strengths in development, manufacturing, and distribution. In the future, Hitachi intends to intensify and expand these initiatives on DX and to establish a new value chain for regenerative medicine products as a means of helping achieve personalized healthcare where all patients can choose the therapies that are best for them.





With the emergence of such new modalities as immunotherapy, cell therapy, and nuclear medicine along with genetic testing, companion diagnostic agents, and other advanced testing and diagnostic techniques, the 21st century is ushering in a new era of personalized healthcare where everyone has access to therapies selected on the basis of their individual circumstances. Among these new medical practices and drugs, one area that shows particular promise for improving patient quality of life (QoL) is that of “regenerative medicine and related products.” This term refers to therapeutic products or agents that are derived from the patient’s own or a donor’s cells or tissue. In North America and Europe in particular, it is a field of ongoing development with a focus on conditions such as cancer or the central nervous system where there is a low level of satisfaction with existing medicines. Only now emerging from its nascent stage, the global market for these products is predicted to grow from around $US80 billion in 2019 to $US360 billion in 2026(1).
As the field of regenerative medicine and related products deals with cells and tissues, it requires the establishment of a new value chain that is managed separately from that for existing pharmaceuticals, which are primarily chemical substances, encompassing materials procurement and handling as well as special manufacturing processes. For example, cells harvested from a patient and the associated profile information need to be passed along to the various participants in this value chain, namely the hospital, transportation provider, and the pharmaceutical manufacturer and its sub-contractors, and this needs to be done in a way that ensures strict accuracy in patient identification while at the same time preserving the anonymity of their personal information. The need for coordination of information between the different industry participants is requiring a revolution in how the value chain is managed.
To this end, Hitachi is drawing on the expertise in IT and operational technology (OT) that it has built up in the healthcare sector to undertake the digital transformation (DX) of the various customer activities that take place along the regenerative medicine value chain. This article focuses on development, manufacturing, and distribution, areas in which Hitachi is particularly strong, presenting overviews and future outlook of three DX solutions that Hitachi has been developing through collaborative creation (co-creation) with pharmaceutical companies. The solutions presented are a DX solution for biomarker discovery, a DX solution for manufacturing regenerative medicine, and a DX platform for supply chain management for regenerative medicine.
Figure 1 — Features of AI Used in Hitachi Digital Solution for Pharma/Biomarker Discovery Service 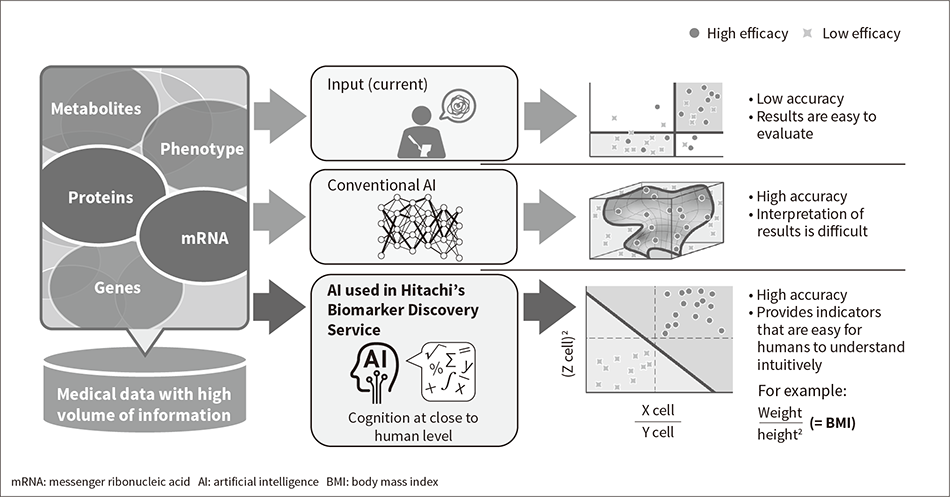 The AI used in Hitachi’s Biomarker Discovery Service automatically generates biomarker candidates with high accuracy and in a way that people can intuitively understand, something that has proved difficult for the AI and manual discovery techniques used in the past.
The AI used in Hitachi’s Biomarker Discovery Service automatically generates biomarker candidates with high accuracy and in a way that people can intuitively understand, something that has proved difficult for the AI and manual discovery techniques used in the past.
The objective of personalized healthcare is to maximize therapeutic efficacy and minimize side effects by providing therapies that are tailored to the patient’s individual characteristics and state of health. Moreover, to be able to select which therapies best suit a particular patient, criteria are needed by which to evaluate the efficacy and safety of specific therapies when used on that patient. Biological indicators that serve this purpose are called “biomarkers” and the identification of suitable candidates forms a major part of the ongoing research aimed at realizing personalized healthcare. While the practice over recent years has been to look for biomarkers in the results of gene and protein analyses, a consensus is building around the idea that, rather than using single genes or proteins, biomarkers that take the form of a combination of different genes or proteins will be needed if the efficacy and safety of specific therapies are to be predicted with high accuracy. Moreover, whereas the quantity of information generated by the analyses of genes or proteins numbers in the thousands or tens of thousands, the number of combinations of genes or proteins runs into the tens or hundreds of millions. Looking for biomarkers that can accurately predict therapeutic efficacy and safety in this huge pool of possible combinations is very difficult if done manually.
Hitachi has developed the Hitachi Digital Solution for Pharma(2)/Biomarker Discovery Service to perform this task with high accuracy by means of artificial intelligence (AI). The service was launched in October 2019(3). The AI used by the service automatically generates biomarkers for accurate efficacy prediction by first identifying which factors are important for predicting the efficacy and side effects of therapies based on patient data from sources such as clinical research and trials, and then by combining these factors into simple equations (see Figure 1). The technique received a Good Design Award in October 2020 in recognition for the ease with which these auto-generated indicators can be interpreted(4). The service has already been used by a number of pharmaceutical companies and research institutions where it has contributed to the discovery of new biomarkers(5). While the conventional approach to biomarker discovery has been hypothesis-driven, the service offers a data-driven approach that is free of cognitive bias and as such has the potential to identify biomarker candidates that would in the past have been difficult to find.
The plan for the future is to integrate the service with the other solutions in the Hitachi Digital Solution for Pharma suite that support business efficiency improvement in the pharmaceutical and medical equipment industries, and to develop a solution that will be able to provide a medical basis for why the biomarker candidates identified by AI were selected. This should shorten the time it currently takes to screen AI-identified biomarker candidates for suitability. By helping to shorten the time and improve the probability of discovering highly accurate biomarkers, Hitachi hopes to bring forward the realization of personalized healthcare that provides each patient with the therapies that are best for them.
Figure 2 — Hands-free SOPs Provided by Hitachi Pharmaceutical Plant Management System 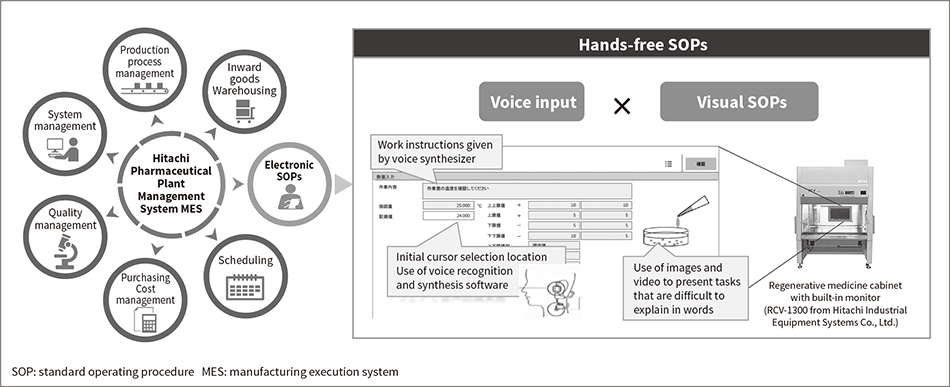 Hitachi has further developed the electronic SOPs that are already in practical use to provide hands-free SOPs that can be performed even when both hands are unavailable. This is done using voice input along with visual SOPs featuring images and video.
Hitachi has further developed the electronic SOPs that are already in practical use to provide hands-free SOPs that can be performed even when both hands are unavailable. This is done using voice input along with visual SOPs featuring images and video.
Pharmaceutical plants seek to optimize their manufacturing processes through innovation and improvement driven by digital technology. Regenerative medicine and related products make up one such sector where explosive market growth is expected, with the use of digital technology to support or replace manual work being seen as an effective way to achieve reliable and high-quality production. With this comes a demand for DX solutions that meet the specific requirements of regenerative medicine. This section describes a manufacturing execution system (MES) for regenerative medicine and related products that forms part of Hitachi’s DX solution for manufacturing regenerative medicine.
How to put manufacturing management practices in place is one of the challenges facing the regenerative medicine industry as it experiences rapid market growth. The production of regenerative medicine and related products differs in many ways from that of regular pharmaceuticals. Specifically, achieving reliable high-volume production calls for more detailed information collection and greater flexibility of response than provided by past manufacturing management practices, including the acquisition of detailed quality records from the production workplace and the ability to modify operating practices based on the quality of individual items.
Hitachi has for a long time been supplying an MES software package for pharmaceutical manufacturing called the Hitachi Pharmaceutical Plant Management System. This MES provides an information network that spans the entire production process, strengthening management and making a major contribution to higher standards in the production environment. Accordingly, along with the MES providing the systems that are essential to the supply of pharmaceuticals with high quality and reliability, the Hitachi Pharmaceutical Plant Management System has also continued to evolve to be used with a wide variety of products. Hitachi is currently working on enhancing the suite of functions that are compatible with management practices specific to regenerative medicine, one example being hands-free standard operating procedures (SOPs) (see Figure 2). To make this possible, Hitachi adopted voice input and visual SOPs. These hands-free SOPs satisfy the user requirement of avoiding the use of hands to operate a personal computer during cell culturing work, which is needed for ergonomic reasons and to prevent contamination and is of particular importance in regenerative medicine manufacturing. The software has already been installed at approximately 15 sites, including both pharmaceutical manufacturers and research institutions that work in the field of regenerative medicine.
In the future, Hitachi intends to persevere with this work in anticipation of DX extending beyond the management of production facilities to deliver optimization across the entire regenerative medicine industry, while also continuing to develop the MES to better meet customer needs and integrating its operation with other systems.
Figure 3 — Block Diagram of DX Platform for Supply Chain Management for Regenerative Medicine 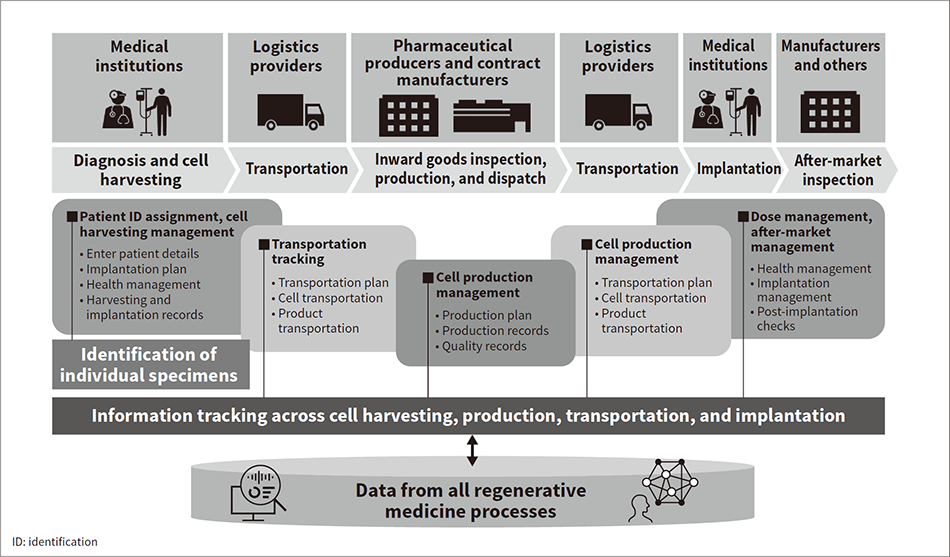 This service platform for the identification of regenerative medicine specimens and integrated management of information tracking across cell harvesting, production, transportation, and implantation is available for use by various stakeholders, including medical institutions, pharmaceutical production, logistics, and manufacturers.
This service platform for the identification of regenerative medicine specimens and integrated management of information tracking across cell harvesting, production, transportation, and implantation is available for use by various stakeholders, including medical institutions, pharmaceutical production, logistics, and manufacturers.
Given that human life depends on the quality of its products, the pharmaceutical industry is expected to maintain strict management of all activities and record keeping along the supply chain. This is particularly true for the distribution of regenerative medicine and related products that include cell-based treatments. Because these involve cultivating cells harvested from the patient or a donor for implantation back into the patient, there is a requirement for information traceability and the tracking of each consignment of cells or other products at every step. This means that information needs to be managed in greater detail than is the case for conventional pharmaceuticals while also sharing information closely between stakeholders.
Recognizing this, Hitachi has drawn on its technology and know-how along with its experience of supplying the industry with production equipment and IT systems to develop and implement a standard platform for supporting optimization across the entire supply chain from cell harvesting through production, transportation, and implantation(6). To ensure versatility and flexibility, the platform has been put together by mixing and matching Hitachi’s existing system components, utilizing its digital twin solution that has already proven itself in information platform and quality traceability applications in manufacturing to cover all activities and record keeping along the supply chain (see Figure 3).
The result is a cloud-based common service platform that is available for use by stakeholders in the regenerative medicine industry, including medical institutions, pharmaceutical production, logistics, and manufacturers. Three examples of the anticipated benefits of adopting and using the platform are as follows.
By providing these benefits, Hitachi is supporting process improvement in supply chain management and helping to make regenerative medicine and related products available with shorter lead times and higher quality.
The platform entered service in January 2021. Following its launch, Hitachi plans to continue enhancing its functions and expanding the scope of system interoperation and data acquisition while also progressively adding new toolsets, including equipment control and the collection of equipment information as well as dynamic scheduling in which the results of data analysis are used as feedback to operations. Through the analysis of data from the supply chain and data on the progress of patients after implantation, Hitachi also intends to make the platform a source of greater value to the people involved in pharmaceuticals by means such as optimizing drug discovery and manufacturing conditions, on-demand delivery, and personalized healthcare.
This article has presented DX solutions in the areas of development, manufacturing, and distribution that provide examples of the work being done by Hitachi in the field of regenerative medicine and related products that are set to become more widely used in the future. Hitachi plans to become more deeply involved in this work in the future, establishing a new value chain for these products by providing even greater support for process improvement by customers. It also intends to contribute to the realization of personalized healthcare where everyone will have access to the therapies that are best for them.