Collaborative Creation with Customers in the US Energy Market
Energy technology innovations under Industrie 4.0 are explosive, fast-paced, and diversified. Technology companies that can adapt to the rapidly evolving digital markets can disrupt the energy industry and quickly gain market share. Vendors are leveraging public grants and external partnerships to speed up the pace of innovation. Co-creation projects with public sector, top research institutes and end-customers including utilities and prosumers can speed up the pace of innovation and validation of solutions to facilitate rapid go-to-market. Hitachi America, Ltd.’s Energy Solution Lab has successfully won several large grants in the past three years and established a new collaboration model with energy stakeholders of different sectors. This article shares Hitachi’s work in the North America market through collaborative creation with customers.




In the past decades, the energy market is evolving driven by green policy initiatives and arising demands of prosumers. As a result, distributed energy resources (DER) become ubiquitous and increasingly dictate the reformation of power grid resource planning and operation. In parallel, the digital technology innovations in the era of Industrie 4.0 are explosive, fast-paced, and diversified. Novel digital energy solutions and their go-to-market strategies need to be agile and iterative. The competition is so intense that enterprise products that fail to address the emerging operational challenges will become obsolete.
While a dynamic market provides tremendous opportunities for business expansion, large corporates often struggle to keep up with the velocity. The Global Center for Social Innovation (CSI) was created to address this challenge. Under CSI, Hitachi America, Ltd.’s (HAL) Energy Solution Laboratory (ESL) has been proactively engaging with industry partners and leverage public research grants, to shorten the development time. This article shares ESL’s latest achievements on eco-system development, innovation philosophy, and institutional coordination.
Collaborative creation (co-creation) with top research institutes can improve Hitachi’s visibility in the technical society and influence trends of innovation. HAL ESL has been proactively responding to calls for the public projects and successfully won two research projects with the United States Department of Energy (DOE) and the State of California from 2018 to 2019. These projects are carefully selected to align with Hitachi’s research program on DER integration, allow necessary customer benchmark and boost internal pace of development.
The mission of HAL ESL is set to develop next generation energy solutions, which can address emerging market needs and potentially grow revenue in five years. This goal concentrates its innovation strategy on integration of existing technologies with some forward-looking core applications.
Back in 2017, the power and energy industry observed rapid rising of renewables and the market for inverter manufacture saturates quickly. HAL ESL decides to look one step beyond the infrastructure value chain and focus on addressing operational challenges introduced by DER. Other major vendors also try to address this emerging market through new enterprise software like distribution management system (DMS), distribution energy resources management system (DERMS), etc., but often found that customers were not satisfied. A recent analysis(1) depicts that deployment of DMS and DERMS in the US market is still in early commercial phase and utility adoptions are slow (see Figure 1). Despite the market potential, existing DMS/DERMS vendors couldn’t provide proper products to address customer needs. HAL ESL found the following:
Figure 1 — Deployment of Operational Analytics 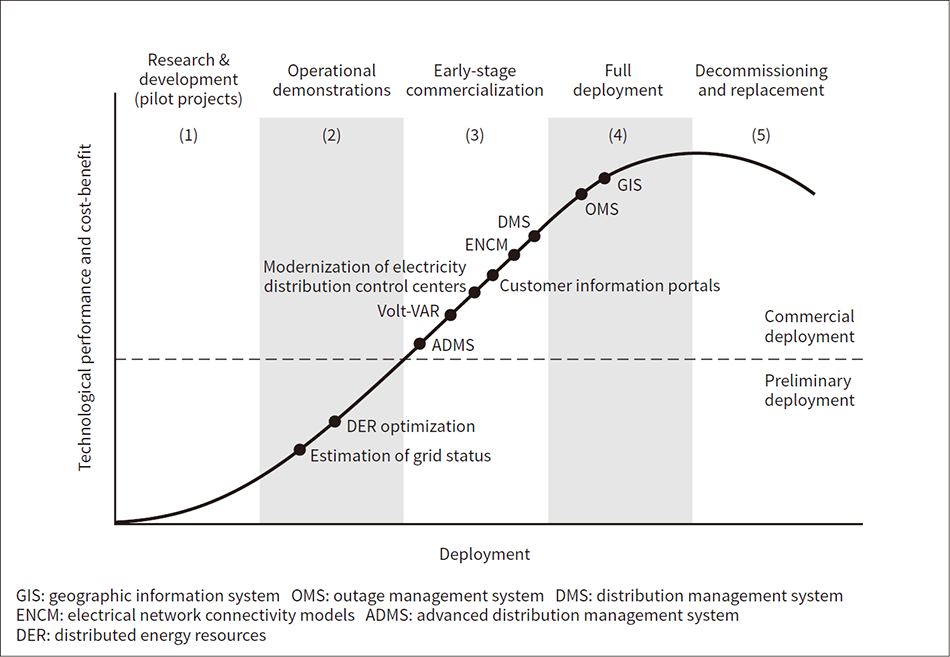 Based on studies by the United States Department of Energy (DOE), the graph plots key aspects of technological innovation in energy management and shows their relative life-cycle stages.
Based on studies by the United States Department of Energy (DOE), the graph plots key aspects of technological innovation in energy management and shows their relative life-cycle stages.
Under these new market trends, HAL ESL decided to focus on creation of a new energy resource optimization solution (see Figure 2). This solution includes the following disruptive technologies:
Figure 2 — Login Screen for Energy Resource Optimization Suite Developed by HAL ESL  The latest Internet of Things (IoT) platform for energy from the Energy Solution Laboratory at Hitachi America, Ltd. (HAL ESL) supports the integration, aggregation, and operation of customer DERs from the public service, commercial, and industrial sectors.
The latest Internet of Things (IoT) platform for energy from the Energy Solution Laboratory at Hitachi America, Ltd. (HAL ESL) supports the integration, aggregation, and operation of customer DERs from the public service, commercial, and industrial sectors.
HAL ESL actively pursue opportunities to strengthen the development of its new energy solutions. It participated in two projects in two consecutive years (2018–2019).
In 2018, the California Energy Commission (CEC)(2) selected HAL to lead a project on DER modeling, recognizing Hitachi’s pioneer efforts developing the new energy resource optimization solution. When CEC observes the rapid increase of DER penetration in California and the reformation of distribution resource planning policies, it foresees equally rapid evolution of planning simulation models and tools. Under the project, HAL ESL creates an intuitive solution, based on its new energy resource optimization solution technologies, which allow all energy stakeholders in California to accurately model solar inverters, EV charging stations, and smart controllable loads, exchange data via secured cloud infrastructure, and analyze impacts of DERs on distribution circuits collaboratively. HAL ESL also steps beyond technology development and develops an innovative engagement model to facilitate frontier policy reformation. This means that HAL ESL needs to engage with a variety of stakeholders including technology partners (SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory), policy execution facilitators (Gridworks) as well as utilities partners including Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E), Southern California Edison (SCE), and National Grid plc.
Then in 2019, the Solar Energy Technology Office (SETO) of the DOE selected 10 project teams to strengthen the integration of solar on the electricity grid(3). The project led by Arizona State University (ASU) is one of them, where HAL ESL is a key team member and the only industry partner. This project will develop a state-of-the-art DER aggregation platform coordinating behind-the-meter (BTM) solar inverters and providing voltage regulation functions to the distribution circuits. Such a platform bridges a gap in industry and compliments existing enterprise systems including DMS and DERMS. The dedicated utility partner, i.e. Arizona Public Services, works closely with Hitachi and provides necessary feedback and system information for technology development.
Under both projects, HAL ESL had opportunities to work with outstanding research institutes, to align with the latest policy initiatives, to develop new applications using its new energy resource optimization solution technologies, and to validate market acceptance with utility customers. The efforts gain great insights at the early technology development stage and greatly shorten tech-to-revenue durations.
The market dynamics in the US energy industry are very different now compared to past decades. To keep up with the rapidly evolving market, HAL ESL adopts a fast-prototype philosophy and leverages participation in public projects to speed up the pace of innovations. Software development cycles are reduced from years to months. Rapid prototypes can obtain customer feedback early on and minimize new product introduction risks. The business product team can then focus on commercial development when initial market exploration is settled and customer requirements for the new product are phased out via the co-creation projects in HAL ESL.
HAL ESL has established strong connections with research communities as a member of the Power Systems Engineering Research Center (PSERC), which provides direct reach to 12 top universities and 26 industry partners. Fortunately, in the latest review with DOE, the HAL project team has received the “All Green” grade, which is considered exceptional for the standard.
HAL ESL will work on research and development of energy solutions to create a sustainable society through co-creation with wide-ranging partners.