1. Establishment of Data Collection Platform for National Hospital Organization Clinical Data Archives
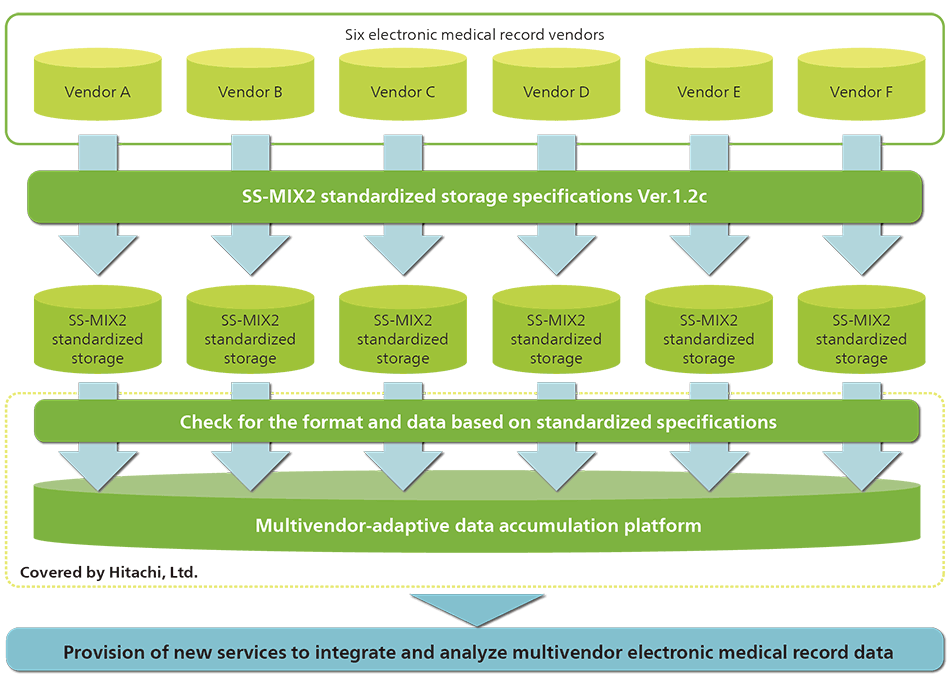
In the business of building the National Hospital Organization Clinical Data Archives (NCDA) conducted by National Hospital Organization (NHO), Hitachi was in charge of constructing the data accumulation platform for the data center.
NCDA collects medical data recorded in daily practice using the standardized structured medical information exchange 2 (SS-MIX2) standardized storage format, the standard specified by Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, without changing the electronic medical record system currently being used in the hospitals under the control of NHO. In addition, diagnosis procedure combination (DPC) evaluation data and medical expenses data accumulated separately will be integrated to create a database that will enable users to effectively analyze large amounts of complicated treatment information and will contribute to improving the quality of medical care and hospital management efficiency.
By making use of the know-how fostered through building the NCDA, Hitachi aims to realize healthcare innovation by providing medical information utilization solutions.