Big Data
We Create (x) byte of data every day
1. Raw Data
Encompasses structured, semistructured and unstructured information
Low Value
2. Optimised Data
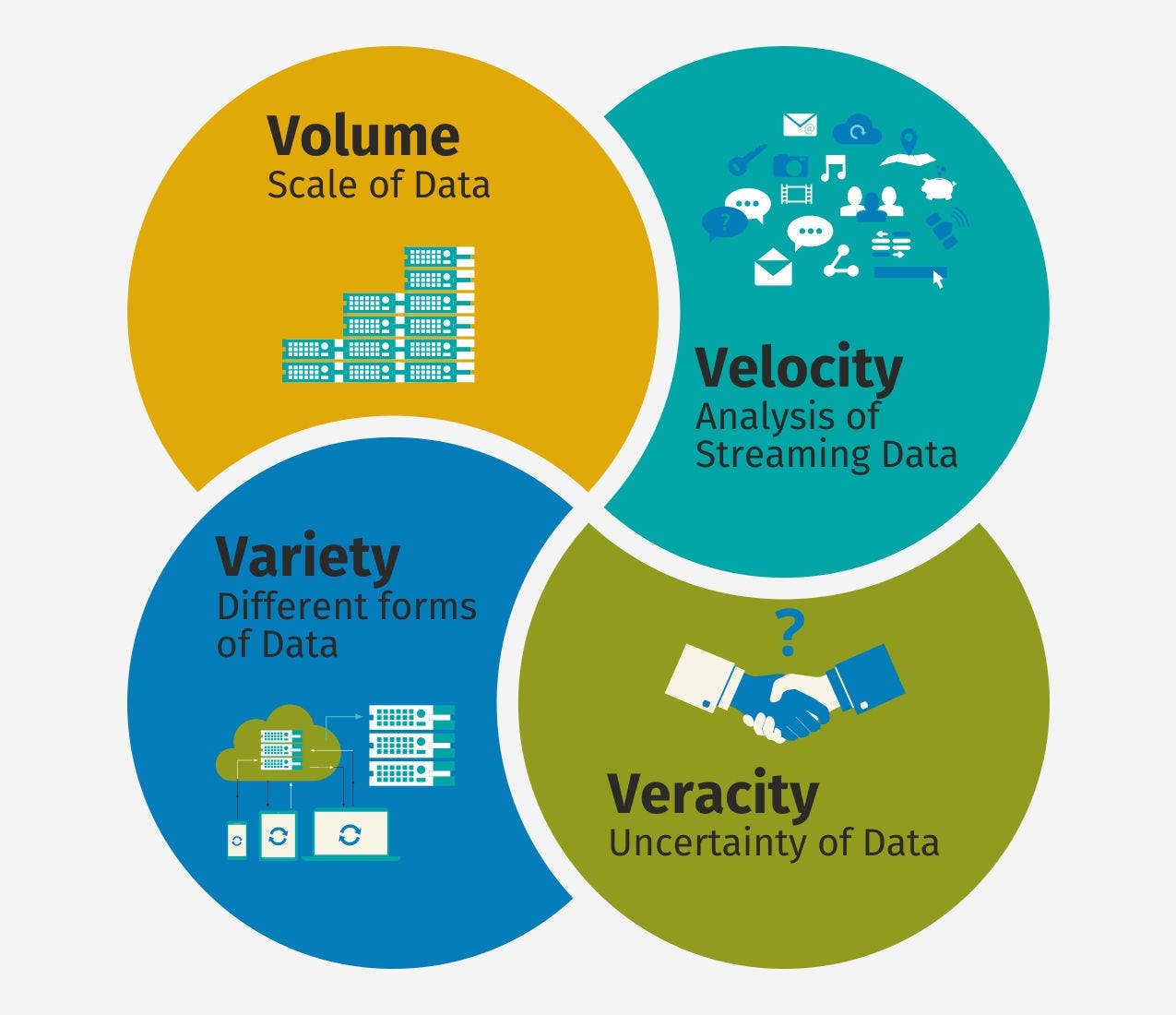
Data has volume (hundreds of petabytes), encompasses velocity (very high speed of storage and analysis), variety (multiple types and sources) and veracity (high quality and trustworthiness)
Create Incremental Value
3. Analysed Data
an be transformed into intelligence to generate value through Analytics technology, tools and skills including (AI) and machine learning (ML)
Create Significant Value
4. New value Data
To create new value in various ways, including interacting with customers, building new products, improving customer service
Amplified Value
The FOUR V’s of Big Data
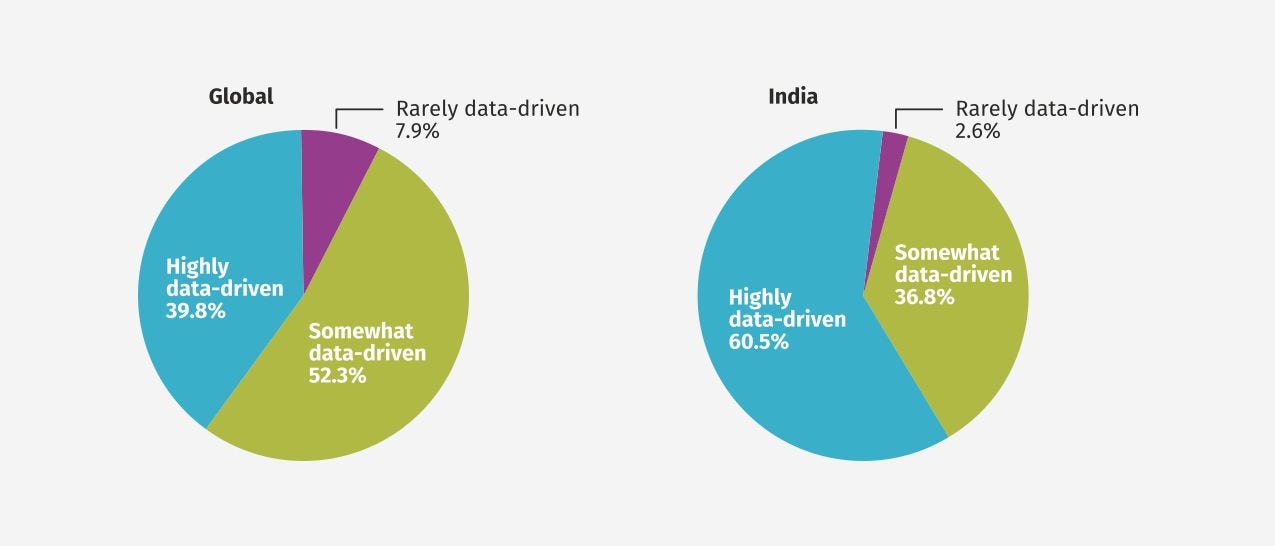
Data Driven Decision Making
Value generation Data Life Cycle
From a functional analysis perspective, various activities are required to be performed to create value from big data, although platform and analytical tool development and other stages are often a precursor.
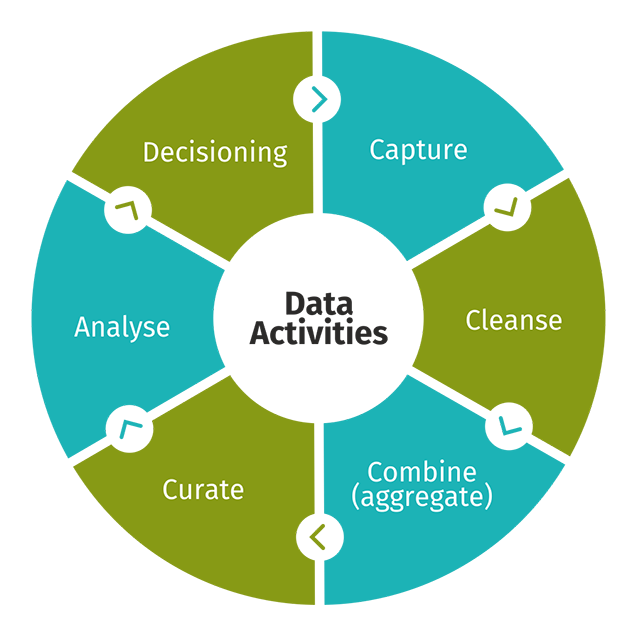
A critical step to gain accurate information. By clearly defining the objective of data analysis raw data is sanitised, thereby accessing relevant and valuable information.
Collating data from multiple sources, comparing and converting them into a common format increases the value of data multi-fold.
Data curation is the process of converting various data sources into unified data sets while maintaining the quality, versatility and flexibility. An important process to make data usable for further analytics.
Today, data analysis combines digital age AI and ML with human expertise to identify important data that needs processing. It is a critical aspect of the data life cycle that that leads to organizational decision making.
For better and faster decisions, businesses can now use advanced analytical techniques such as ML, data mining and statistics to analyse data sources independently or together.
Transform your data into Insights to drive your business

Source:
- PwC Big data : A transfer pricing perspective